22-Jul-2025
Office of Vice President
Why in News?
Vice-president Jagdeep Dhankhar has resigned from his post citing medical reasons, prompting the initiation of the process to select a new vice-president.
About Office of Vice President
- Position in Hierarchy: The Vice President is the second-highest constitutional authority in India, ranking just after the President.
- Order of Precedence: In the official protocol list, the Vice President is ranked directly below the President.
- Inspired by U.S. Model: The office of the Vice President in India is modeled on the American Vice-President's role.
- Role as Acting President: The Vice President acts as the President if the President is unable to perform duties due to death, resignation, removal, or other reasons.
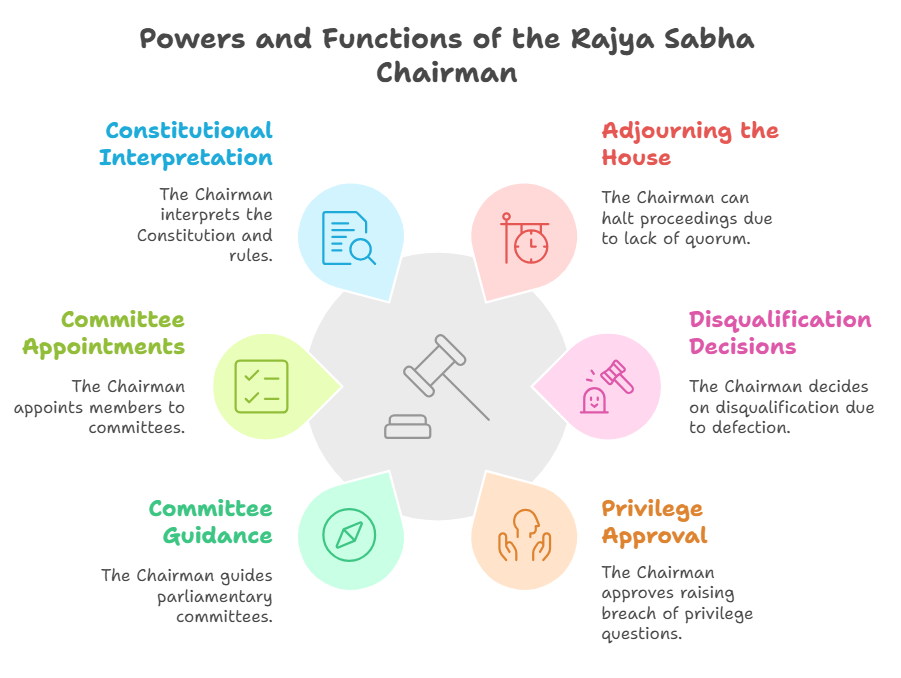
- Chairman of Rajya Sabha: The Vice President also serves as the ex-officio Chairman of the Rajya Sabha, the upper house of Parliament.
Election of the Vice President
- Indirect Election: The Vice President is not elected directly by the people, but through an indirect election process, similar to the President.
- Electoral College Composition: The Vice President is elected by an electoral college made up of members of both Houses of Parliament.
- Difference from Presidential Electoral College
- Includes both elected and nominated members of Parliament (unlike the President’s, which includes only elected members).
- Does not include members of state legislative assemblies (who are included in the Presidential election).
- Election Method: The election is conducted using the proportional representation system through the single transferable vote method.
- Secret Voting: Voting for the Vice President’s election is done through a secret ballot.
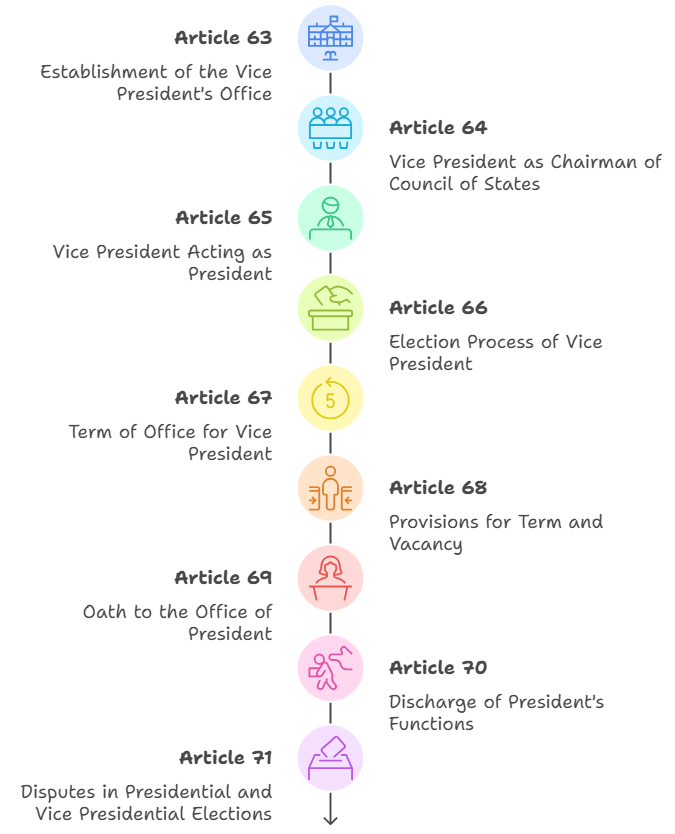
Constitutional Provisions Related to the Vice President of India
Eligibility Criteria for Vice President of India
- Indian Citizenship: The candidate must be a citizen of India.
- Minimum Age: The person should have completed 35 years of age.
- Rajya Sabha Qualification: Must be qualified to be elected as a member of the Rajya Sabha.
- No Office of Profit: The candidate must not hold any office of profit under the Union, State, local, or any other public authority.
Conditions for Holding the Office of Vice President
- No Membership in Legislature
- The Vice President must not be a member of Parliament or any state legislature.
- If elected while holding such a position, the seat is considered automatically vacated on assuming office.
- No Office of Profit: The Vice President must not hold any other office of profit during the term.
Term of Office of the Vice President
- The Vice President serves a term of five years from the date of assuming office.
- He can resign at any time by submitting a resignation letter to the President of India.
Vacancy in the Office of Vice President
A vacancy in the Vice President’s office can arise due to
- Completion of Term
- Resignation
- Removal
- Death
- Otherwise
Removal of the Vice President of India
- No Impeachment Required: The Vice President can be removed without a formal impeachment process.
- Procedure
- A resolution must be passed in the Rajya Sabha with an effective majority (majority of the total membership, excluding vacancies).
- It must then be approved by the Lok Sabha with a simple majority (majority of members present and voting).
- Initiation: The resolution can only be introduced in the Rajya Sabha, not in the Lok Sabha.
- Notice Period: At least 14 days' prior notice must be given before moving the resolution.
Preparing Through MCQ
Q. Which of the following statements about the Vice President of India is correct?
(1) The Vice President is directly elected by the people of India.
(2) The Vice President also serves as the Speaker of the Lok Sabha.
(3) The Vice President is elected by an electoral college including state legislative assemblies.
(4) The Vice President is elected by an electoral college consisting of both elected and nominated members of Parliament.
Answer: (4) The Vice President is elected by an electoral college consisting of both elected and nominated members of Parliament.